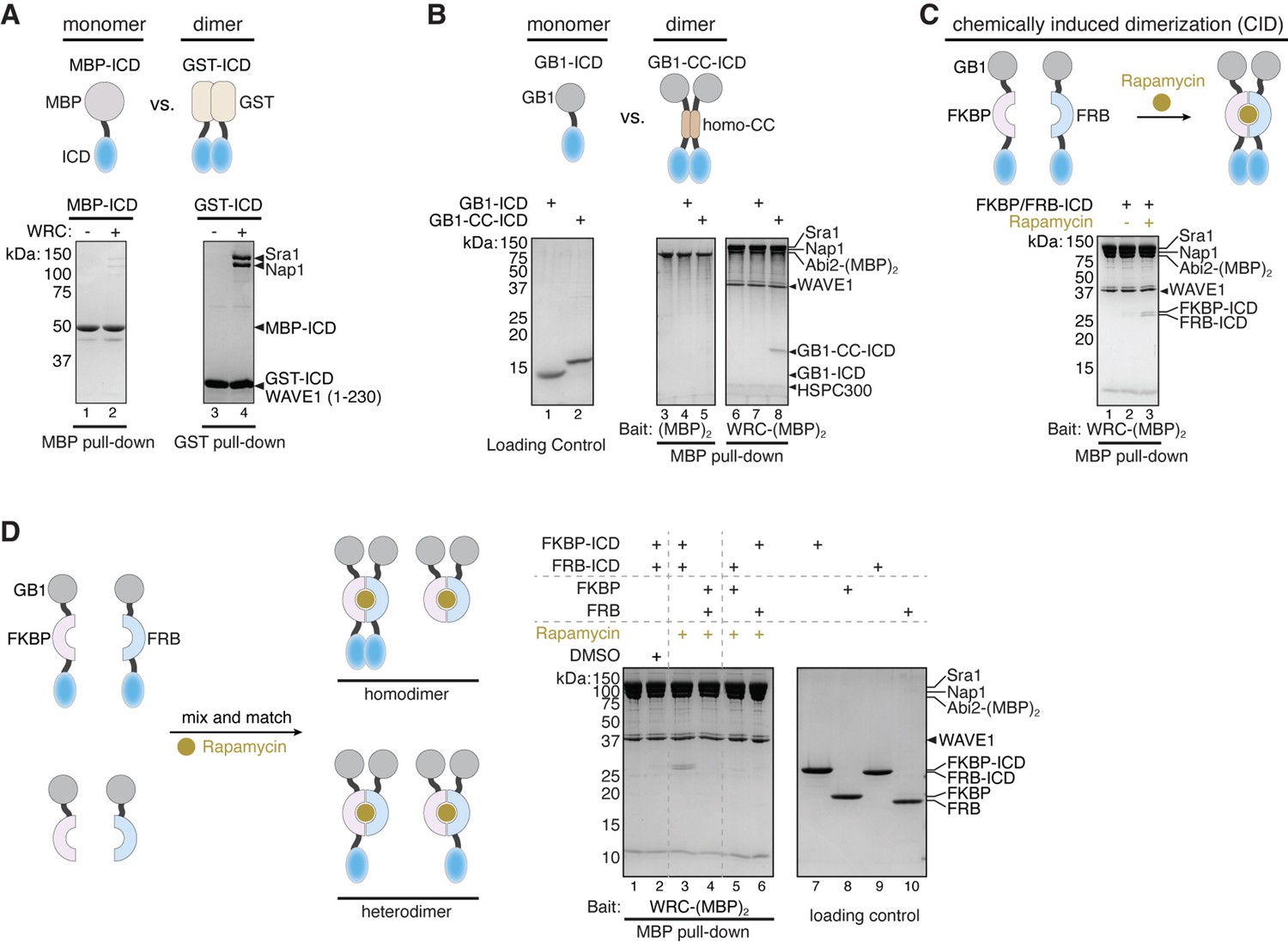
Rac1 Regulates Neuronal Polarization through the WAVE Complex
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 dezembro 2024

Neuronal migration and axon growth, key events during neuronal development, require distinct changes in the cytoskeleton. Although many molecular regulators of polarity have been identified and characterized, relatively little is known about their physiological role in this process. To study the physiological function of Rac1 in neuronal development, we have generated a conditional knock-out mouse, in which Rac1 is ablated in the whole brain. Rac1 -deficient cerebellar granule neurons, which do not express other Rac isoforms, showed impaired neuronal migration and axon formation both in vivo and in vitro . In addition, Rac1 ablation disrupts lamellipodia formation in growth cones. The analysis of Rac1 effectors revealed the absence of the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family verprolin-homologous protein (WAVE) complex from the plasma membrane of knock-out growth cones. Loss of WAVE function inhibited axon growth, whereas overexpression of a membrane-tethered WAVE mutant partially rescued axon growth in Rac1 -knock-out neurons. In addition, pharmacological inhibition of the WAVE complex effector Arp2/3 also reduced axon growth. We propose that Rac1 recruits the WAVE complex to the plasma membrane to enable actin remodeling necessary for axon growth.

Membrane-targeted WAVE mediates photoreceptor axon targeting in the absence of the WAVE complex in Drosophila

Journal of Cellular Physiology, Cell Biology Journal
Cells, Free Full-Text

PDF) Rac1 plays an essential role in axon growth and guidance and in neuronal survival in the central and peripheral nervous systems
The intrinsically disordered cytoplasmic tail of a dendrite branching receptor uses two distinct mechanisms to regulate the actin cytoskeleton
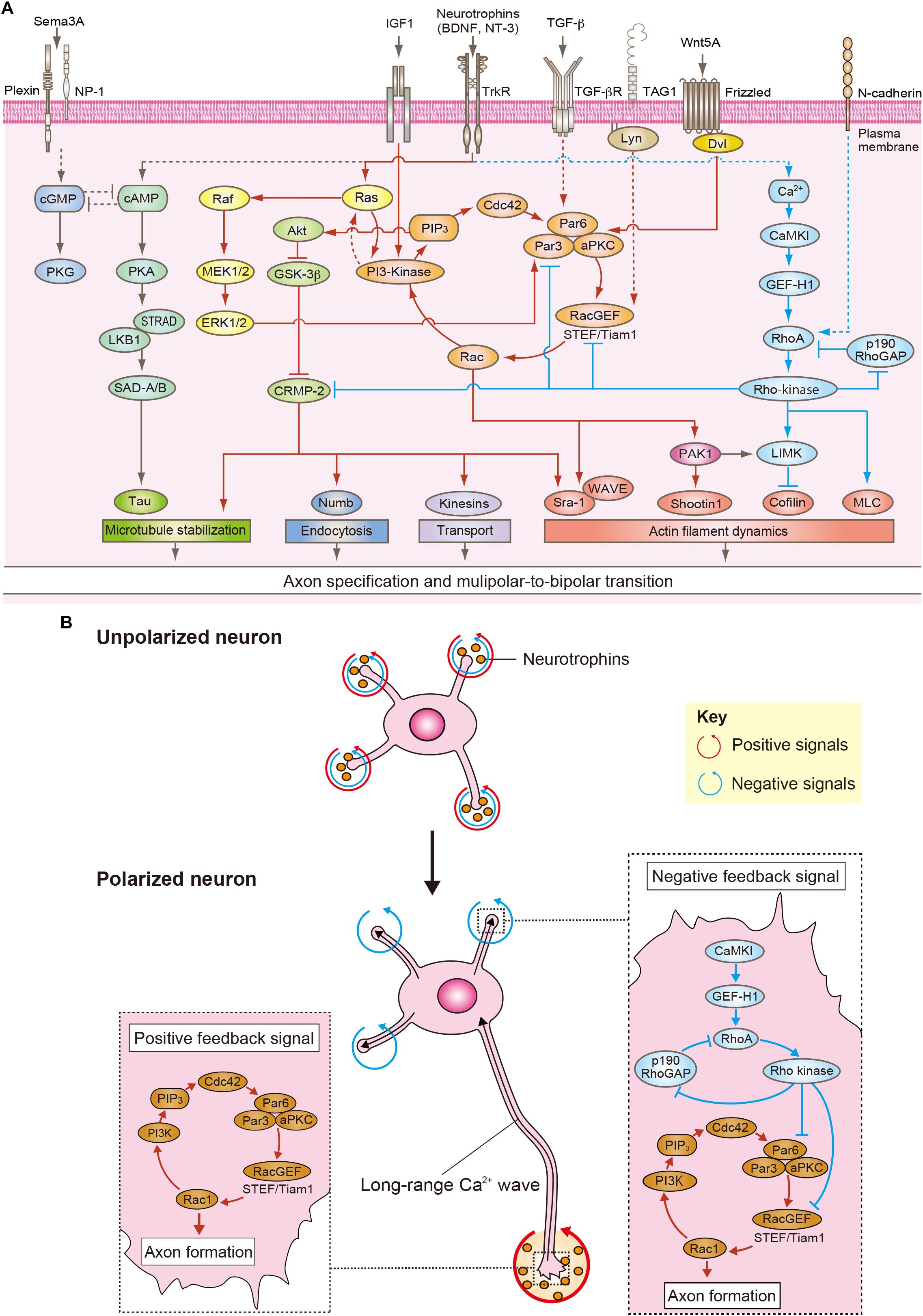
Frontiers Neuronal Polarity: Positive and Negative Feedback Signals

Neuronal actin cytoskeleton gain of function in the human brain - eBioMedicine
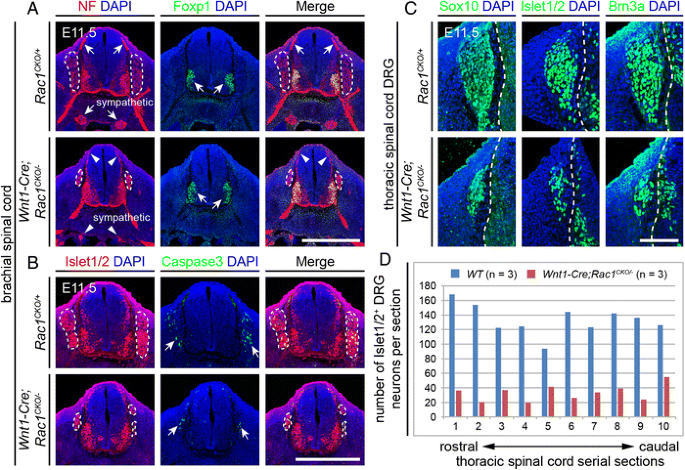
Rac1 plays an essential role in axon growth and guidance and in neuronal survival in the central and peripheral nervous systems, Neural Development

Development of neuronal polarity in vivo - ScienceDirect
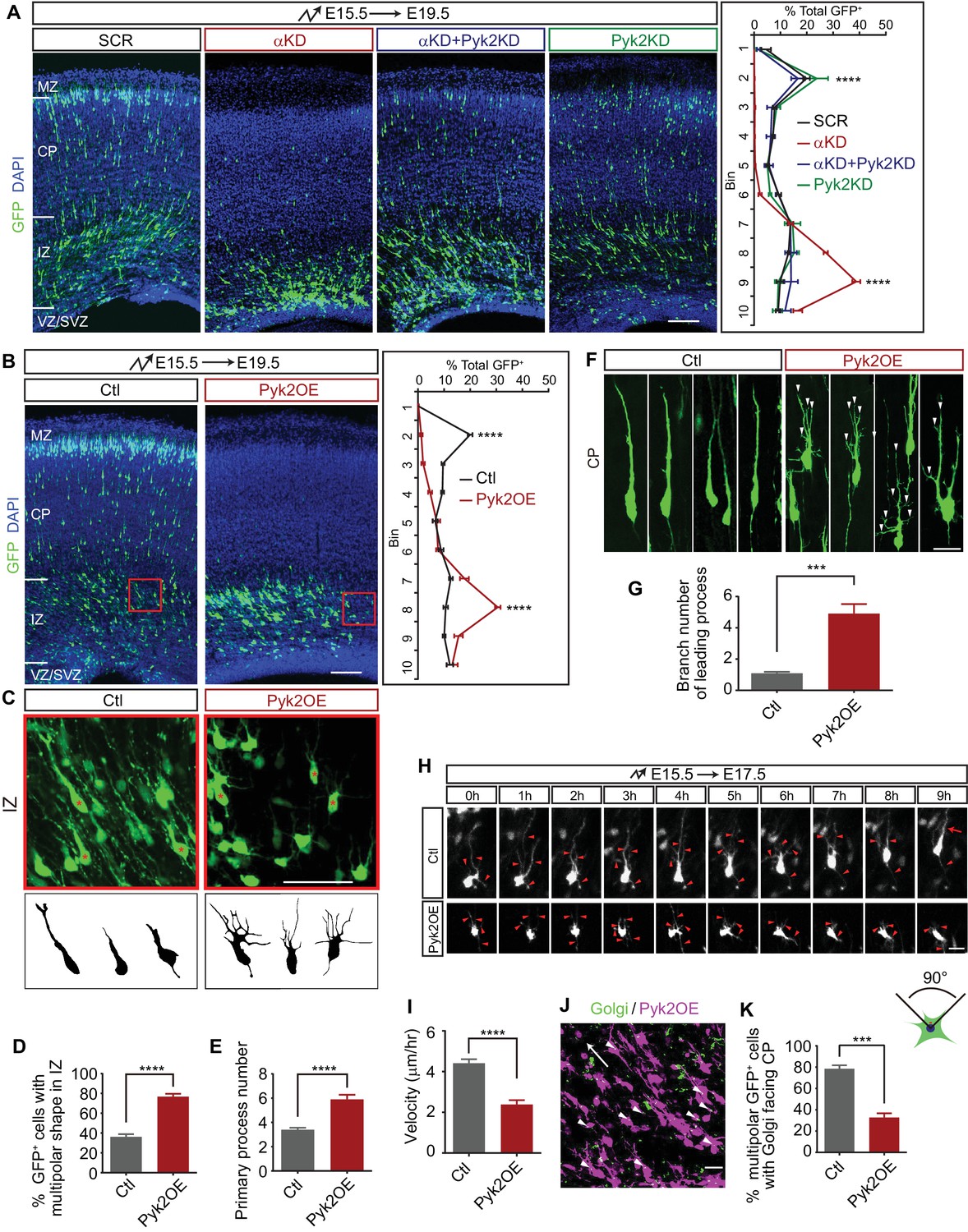
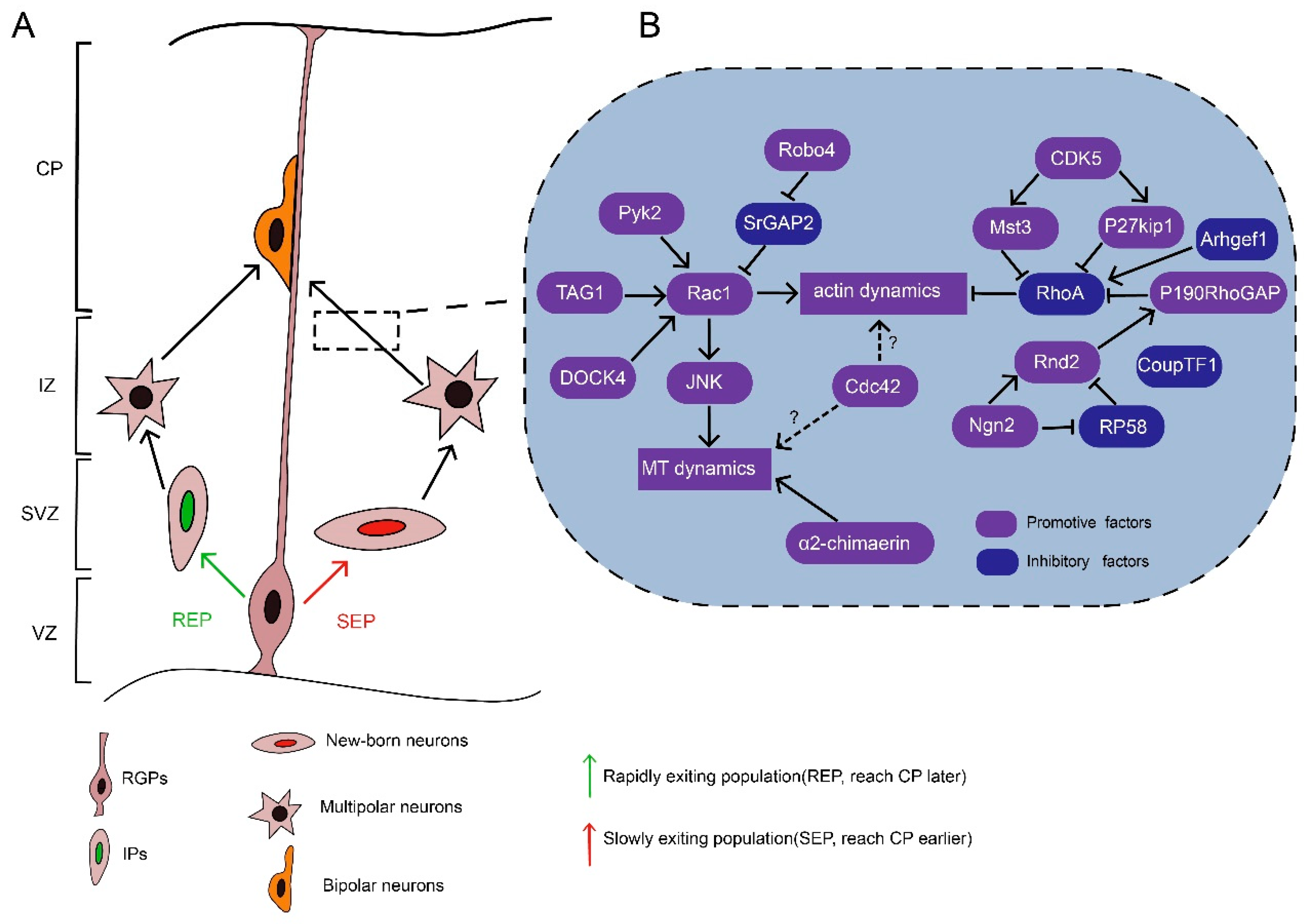
Alpha protocadherins and Pyk2 kinase regulate cortical neuron migration and cytoskeletal dynamics via Rac1 GTPase and WAVE complex in mice

Rac1 Regulates Neuronal Polarization through the WAVE Complex

Coronin 2B Regulates Neuronal Migration via Rac1-Dependent Multipolar–Bipolar Transition
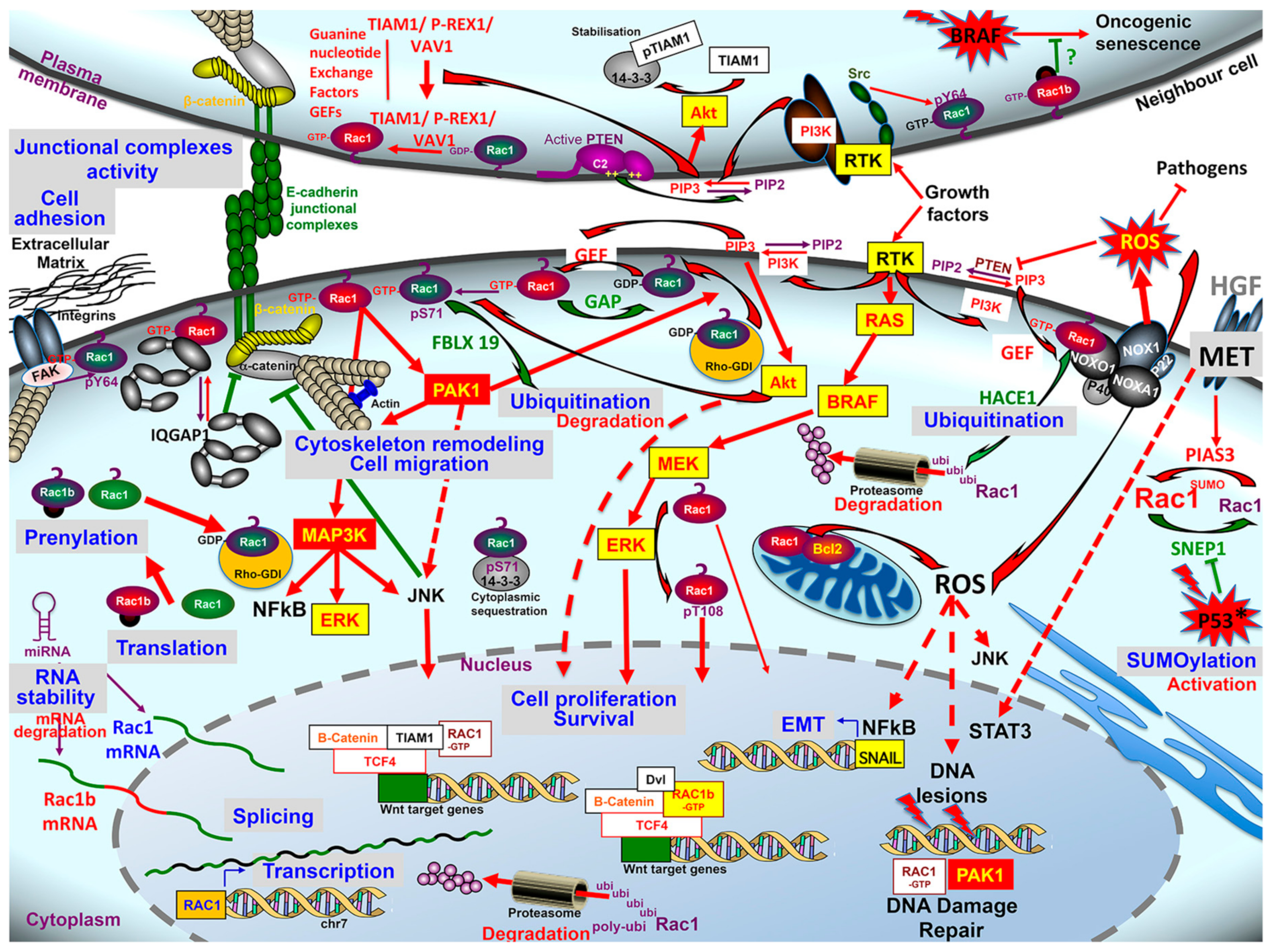
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Neuronal Polarity: Positive and Negative Feedback Signals. - Abstract - Europe PMC
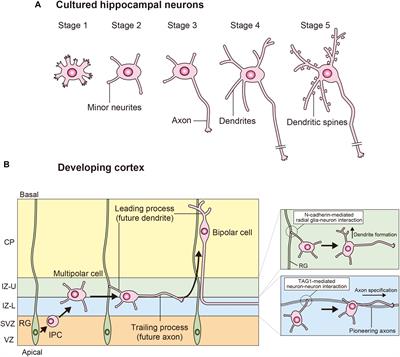
Frontiers Neuronal Polarity: Positive and Negative Feedback Signals
Recomendado para você
-
Urs campeão? #mrolympia #cbum31 dezembro 2024
-
Quando o wave liga a live PARTE 1🤣🤣#foryou #funnyvideos #tilt #csgo31 dezembro 2024
-
 Astrocyte recruitment is augmented within the calcium wave in the VPA31 dezembro 2024
Astrocyte recruitment is augmented within the calcium wave in the VPA31 dezembro 2024 -
 Wave Consultancy & Event Hut in Mohan Nagar,Delhi - Best Placement Services (For Employers) in Delhi - Justdial31 dezembro 2024
Wave Consultancy & Event Hut in Mohan Nagar,Delhi - Best Placement Services (For Employers) in Delhi - Justdial31 dezembro 2024 -
 JBL Wave Buds Fone de ouvido TWS JBL31 dezembro 2024
JBL Wave Buds Fone de ouvido TWS JBL31 dezembro 2024 -
Gui Moraes - Professor particular de inglês no Cambly31 dezembro 2024
-
 Prepared to Surf - oferece versão em inglês31 dezembro 2024
Prepared to Surf - oferece versão em inglês31 dezembro 2024 -
 A Gazeta Com apenas dois anos, garotinho de Guarapari já sabe ler e até somar31 dezembro 2024
A Gazeta Com apenas dois anos, garotinho de Guarapari já sabe ler e até somar31 dezembro 2024 -
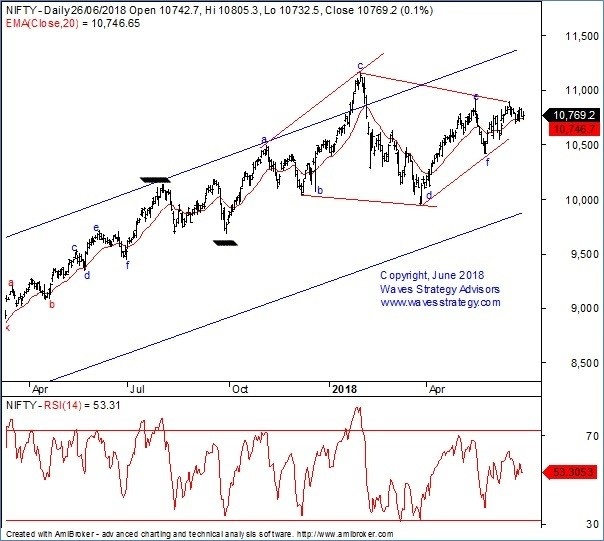 Nifty: How to trade Neo wave Diametric pattern?31 dezembro 2024
Nifty: How to trade Neo wave Diametric pattern?31 dezembro 2024 -
 Mario Kart 8 Deluxe's second wave of DLC tracks revealed: All Booster Course Pass tracks - Dexerto31 dezembro 2024
Mario Kart 8 Deluxe's second wave of DLC tracks revealed: All Booster Course Pass tracks - Dexerto31 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Articuno builder by thatmetalguy1011 on DeviantArt31 dezembro 2024
Articuno builder by thatmetalguy1011 on DeviantArt31 dezembro 2024 -
SVG > answer avatar person guide - Free SVG Image & Icon.31 dezembro 2024
-
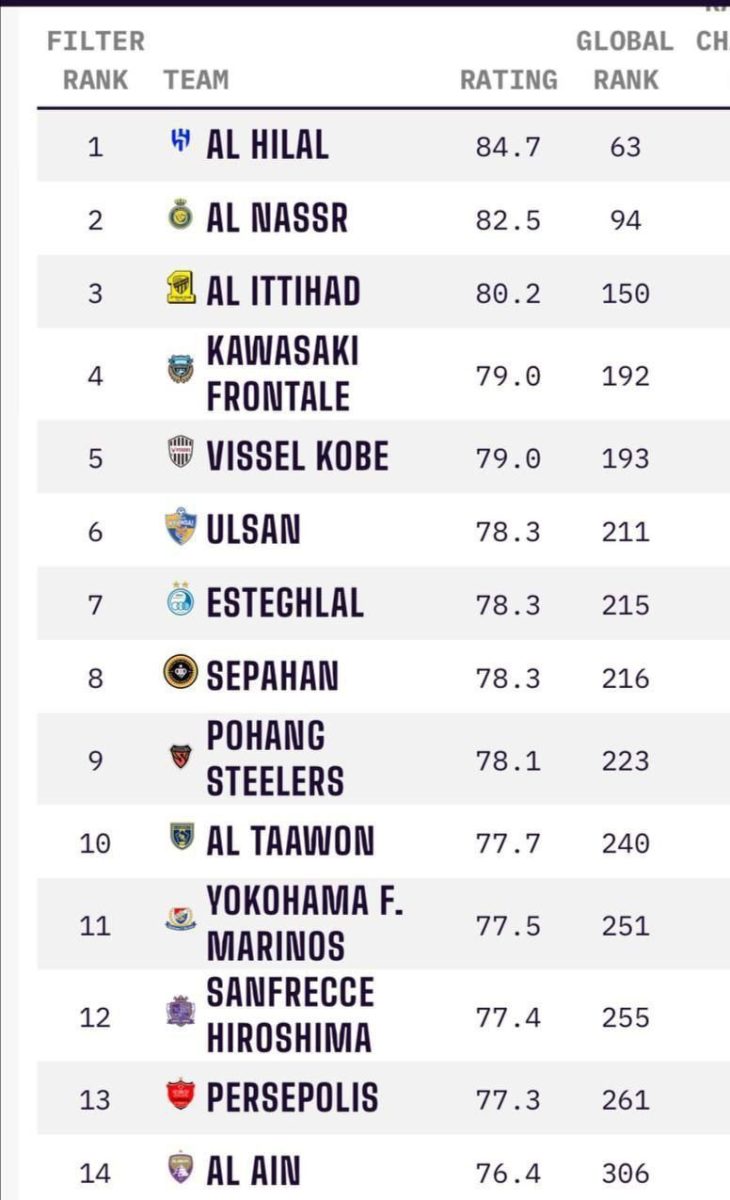 Iran's Esteghlal, Sepahan Ranked Among Top Ten Football Teams In Asia - Iran Front Page31 dezembro 2024
Iran's Esteghlal, Sepahan Ranked Among Top Ten Football Teams In Asia - Iran Front Page31 dezembro 2024 -
 Pin by 2019A on صورة Instagram profile picture ideas, Instagram31 dezembro 2024
Pin by 2019A on صورة Instagram profile picture ideas, Instagram31 dezembro 2024 -
 Doando Ocs ( 𝙂𝙖𝙘𝙝𝙖 𝘾𝙡𝙪𝙗 ) 🎧31 dezembro 2024
Doando Ocs ( 𝙂𝙖𝙘𝙝𝙖 𝘾𝙡𝙪𝙗 ) 🎧31 dezembro 2024 -
 Baixe Minecraft Pocket Edition 1.0.8 (Sem erro de análise31 dezembro 2024
Baixe Minecraft Pocket Edition 1.0.8 (Sem erro de análise31 dezembro 2024 -
 Best puffer jackets for men 2023: Uniqlo to Moncler31 dezembro 2024
Best puffer jackets for men 2023: Uniqlo to Moncler31 dezembro 2024 -
 senzie 🐰 on X: 💄sensaur x @pastelicheart makeup set! 3 new cute31 dezembro 2024
senzie 🐰 on X: 💄sensaur x @pastelicheart makeup set! 3 new cute31 dezembro 2024 -
 Part 1: Double Cross, Shadowrun: Excommunication31 dezembro 2024
Part 1: Double Cross, Shadowrun: Excommunication31 dezembro 2024 -
 Redfall apresenta trailer focado na história de Jacob Boywer31 dezembro 2024
Redfall apresenta trailer focado na história de Jacob Boywer31 dezembro 2024

