Nutrients, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 dezembro 2024
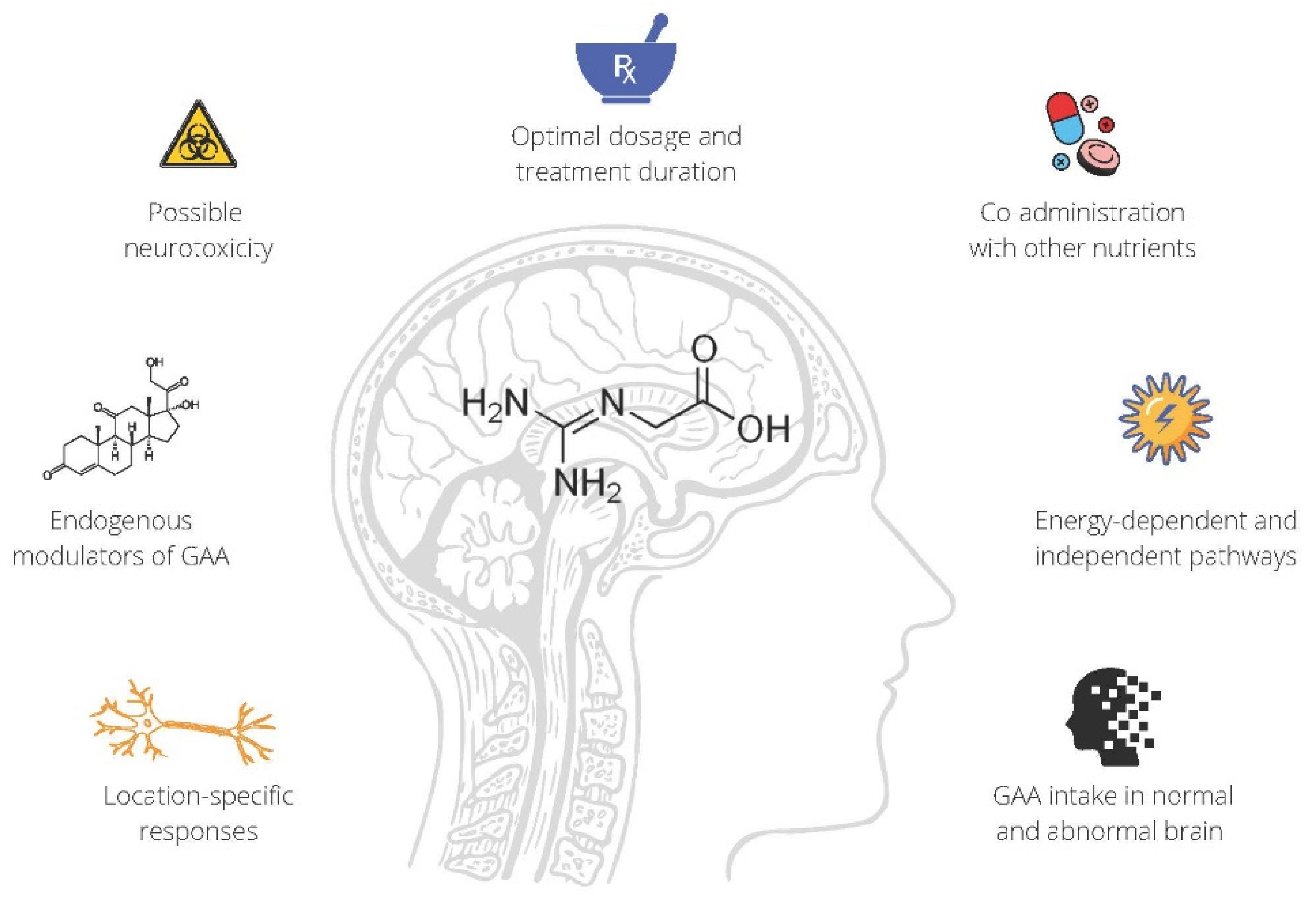
While the vast majority of research involving creatine supplementation has focused on skeletal muscle, there is a small body of accumulating research that has focused on creatine and the brain. Preliminary studies indicate that creatine supplementation (and guanidinoacetic acid; GAA) has the ability to increase brain creatine content in humans. Furthermore, creatine has shown some promise for attenuating symptoms of concussion, mild traumatic brain injury and depression but its effect on neurodegenerative diseases appears to be lacking. The purpose of this narrative review is to summarize the current body of research pertaining to creatine supplementation on total creatine and phophorylcreatine (PCr) content, explore GAA as an alternative or adjunct to creatine supplementation on brain creatine uptake, assess the impact of creatine on cognition with a focus on sleep deprivation, discuss the effects of creatine supplementation on a variety of neurological and mental health conditions, and outline recent advances on creatine supplementation as a neuroprotective supplement following traumatic brain injury or concussion.

Nutrients, Free Full-Text, Evolution of the Human Diet and Its Impact on Gut Microbiota, Immune Responses, and Br…
Nutrients, Free Full-Text

MyPlate U.S. Department of Agriculture
Nutrients An Open Access Journal from MDPI
What is Food Nutrition Scale Data Entry? - ITS
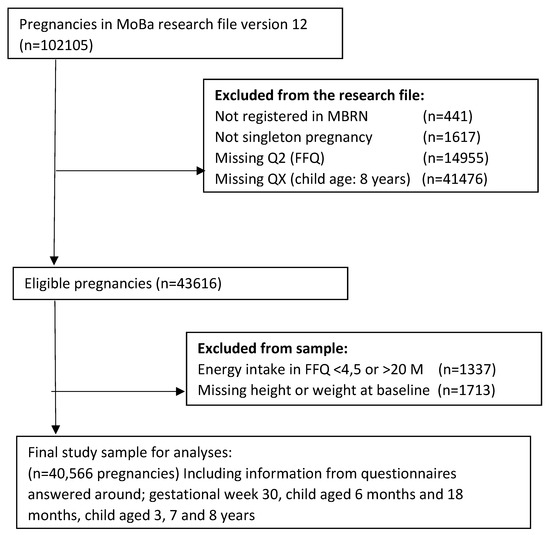
Pregnancy Chart Get File - Colaboratory
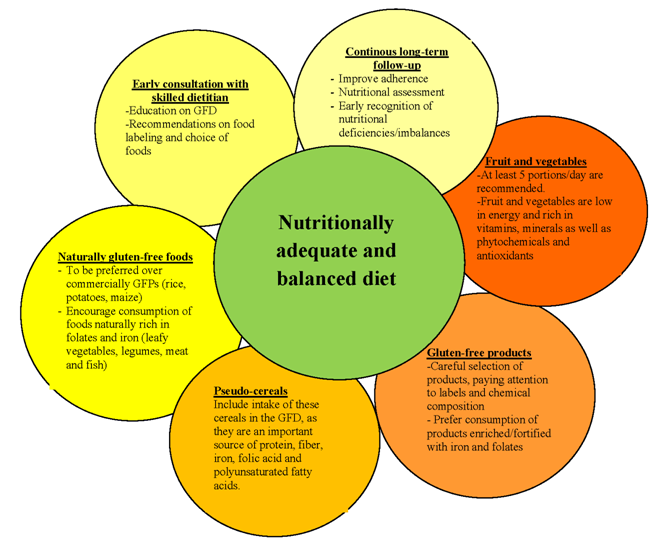
Gluten Free Diet Attention - Colaboratory
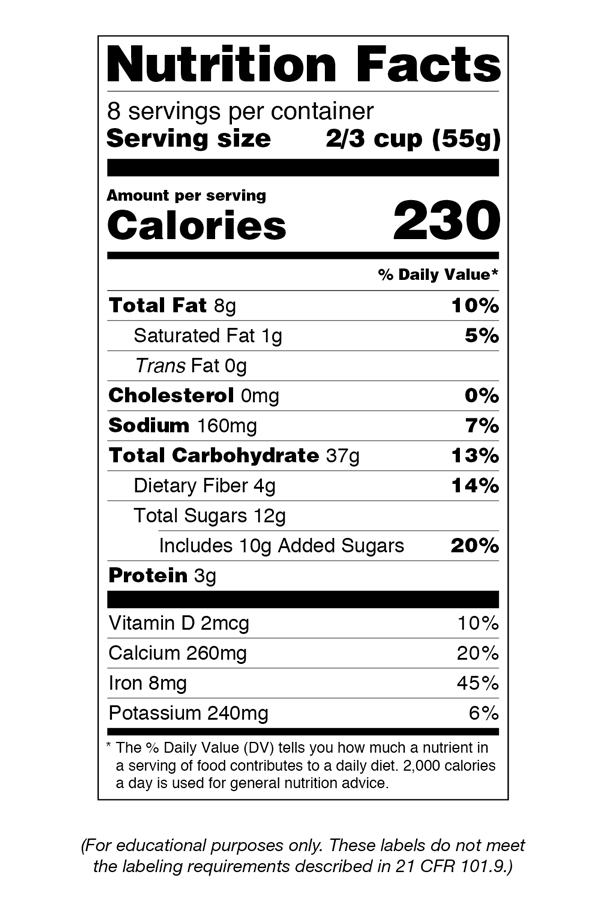
Nutrition Facts Label Images for Download
Food Science & Nutrition - Wiley Online Library
Recomendado para você
-
 Results of whole brain analyses in the test scan. a The left parietal22 dezembro 2024
Results of whole brain analyses in the test scan. a The left parietal22 dezembro 2024 -
 Test your brain power on Zoom in August! - General News - News22 dezembro 2024
Test your brain power on Zoom in August! - General News - News22 dezembro 2024 -
 Brain Test Уровень 367 ответы (Он хочет большие мышцы)22 dezembro 2024
Brain Test Уровень 367 ответы (Он хочет большие мышцы)22 dezembro 2024 -
 Lengkap Ada Video, Brain Test Level 367 Saatnya Mancari cuan! ✓22 dezembro 2024
Lengkap Ada Video, Brain Test Level 367 Saatnya Mancari cuan! ✓22 dezembro 2024 -
 Brain Test: Tricky Puzzles Answers for All Levels - Page 37 of 46 - Level Winner22 dezembro 2024
Brain Test: Tricky Puzzles Answers for All Levels - Page 37 of 46 - Level Winner22 dezembro 2024 -
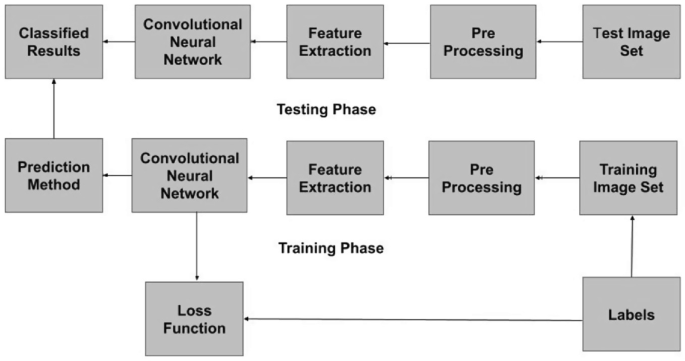 Automatic Brain Tumor Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks22 dezembro 2024
Automatic Brain Tumor Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks22 dezembro 2024 -
 Improving the study of brain-behavior relationships by revisiting basic assumptions: Trends in Cognitive Sciences22 dezembro 2024
Improving the study of brain-behavior relationships by revisiting basic assumptions: Trends in Cognitive Sciences22 dezembro 2024 -
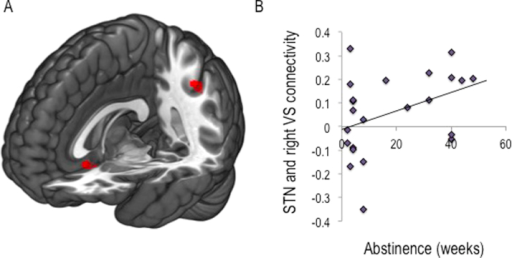 Subthalamic nucleus connectivity in binge drinkers and22 dezembro 2024
Subthalamic nucleus connectivity in binge drinkers and22 dezembro 2024 -
 Evilfan1 User Profile22 dezembro 2024
Evilfan1 User Profile22 dezembro 2024 -
 حل مرحلة brain test 36722 dezembro 2024
حل مرحلة brain test 36722 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Rainbow Friends Stuffed Animals22 dezembro 2024
Rainbow Friends Stuffed Animals22 dezembro 2024 -
 Luffy, one piece, HD phone wallpaper22 dezembro 2024
Luffy, one piece, HD phone wallpaper22 dezembro 2024 -
 GameSpot Reviews - Twisted Metal (PS3)22 dezembro 2024
GameSpot Reviews - Twisted Metal (PS3)22 dezembro 2024 -
 Dia dos Pais 2021: oito jogos de tabuleiro e cartas para presentear e se divertir - Monet22 dezembro 2024
Dia dos Pais 2021: oito jogos de tabuleiro e cartas para presentear e se divertir - Monet22 dezembro 2024 -
Hikaru Nara - Full Score22 dezembro 2024
-
 Os 4 jogos imperdíveis na rodada de Boxing Day da Premier League22 dezembro 2024
Os 4 jogos imperdíveis na rodada de Boxing Day da Premier League22 dezembro 2024 -
 script in blox fruit update 20 for auto cdk|TikTok Search22 dezembro 2024
script in blox fruit update 20 for auto cdk|TikTok Search22 dezembro 2024 -
 Understanding Queen Endgames22 dezembro 2024
Understanding Queen Endgames22 dezembro 2024 -
 Moffat County boys wrestling masters Maverick Duals; girls team sees first-ever tourney22 dezembro 2024
Moffat County boys wrestling masters Maverick Duals; girls team sees first-ever tourney22 dezembro 2024 -
 Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Review: Unrivaled Champion22 dezembro 2024
Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra Review: Unrivaled Champion22 dezembro 2024
